Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Efficacy and safety of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: A case series in China
Lancet 2025 Doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(25)01671-X Epub ahead of print
Gao et al. report that allogeneic CAR NK-cell therapy is a potent option for treatment of autoimmune diseases and may address limitations of current autologous CAR T-cell therapy, including manufacturing scale and time, access, safety, and cost. Authors evaluated the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory SLE.
Keywords:
Low-dose belimumab reduced risk of flares in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Ann Rheum Dis 2025 Doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.10.010. Epub ahead of print
Sun et al. provides the first RCT evidence that low-dose belimumab reduces flares in patients with SLE with low-grade disease activity. Authors evaluated the efficacy of low-dose belimumab for disease flare prevention in Chinese patients with low-grade SLE (SELENA-SLEDAI ≤6).
Keywords:
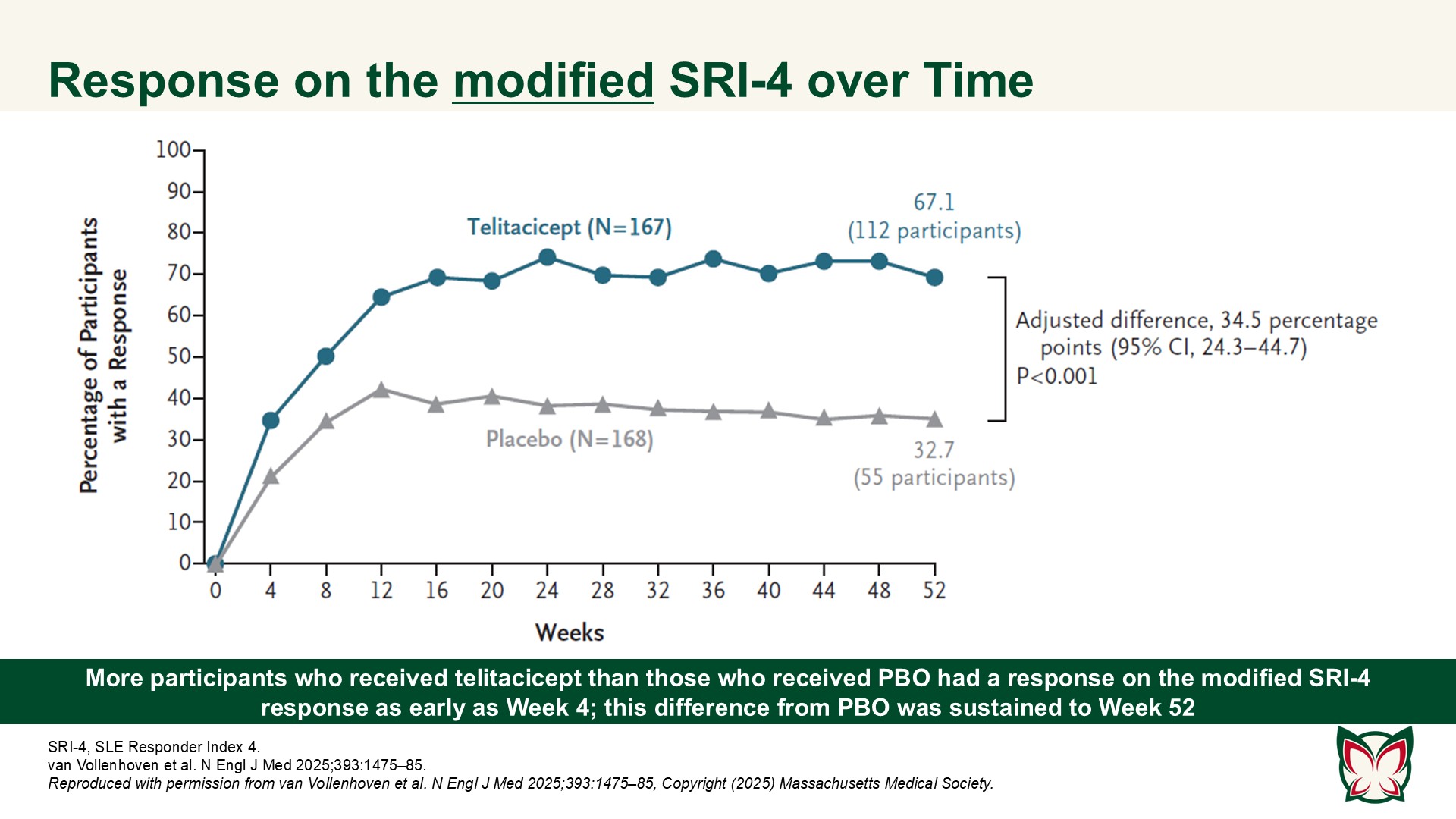
A Phase 3 trial of telitacicept for systemic lupus erythematosus
N Engl J Med 2025;393:1475-85 Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2414719
In this 52-week trial involving participants with active SLE who were receiving background therapy, the incidence of a clinical response was higher with telitacicept than with PBO. van Vollenhoven et al. report efficacy and safety results of a Phase 3 trial of telitacicept at a dose of 160mg weekly as compared with PBO in Chinese persons with active SLE.
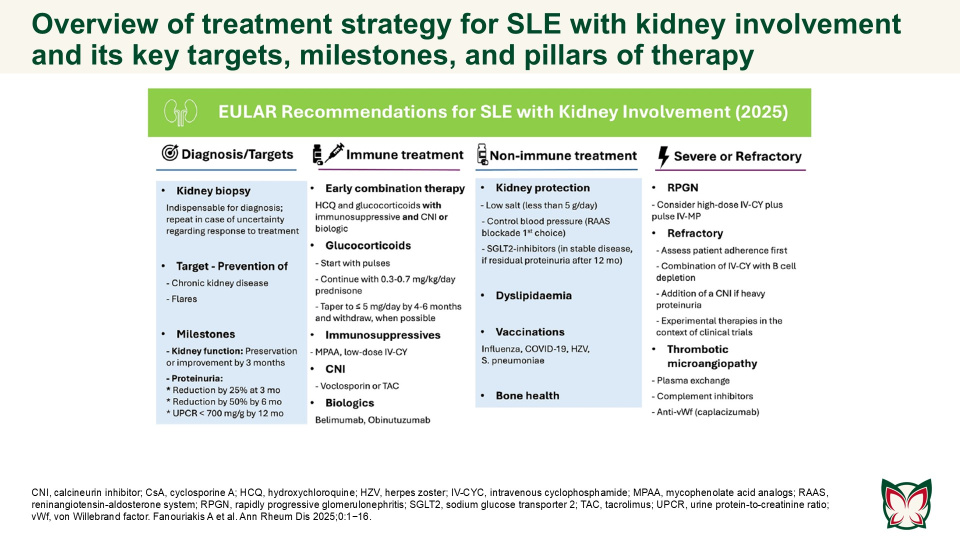
EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus with kidney involvement: 2025 update
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;0:1−16 Doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.09.007
The updated EULAR recommendations provide evidence- and expert-based consensus on the management of SLE with kidney involvement, adjusted for severity, and taking into consideration long-term efficacy, safety, cost, and local availability of drugs. Fanouriakis A et al. updated the 2019 EULAR/ ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of SLE with kidney involvement, taking into consideration emerging evidence and recent developments in the field.
Keywords:
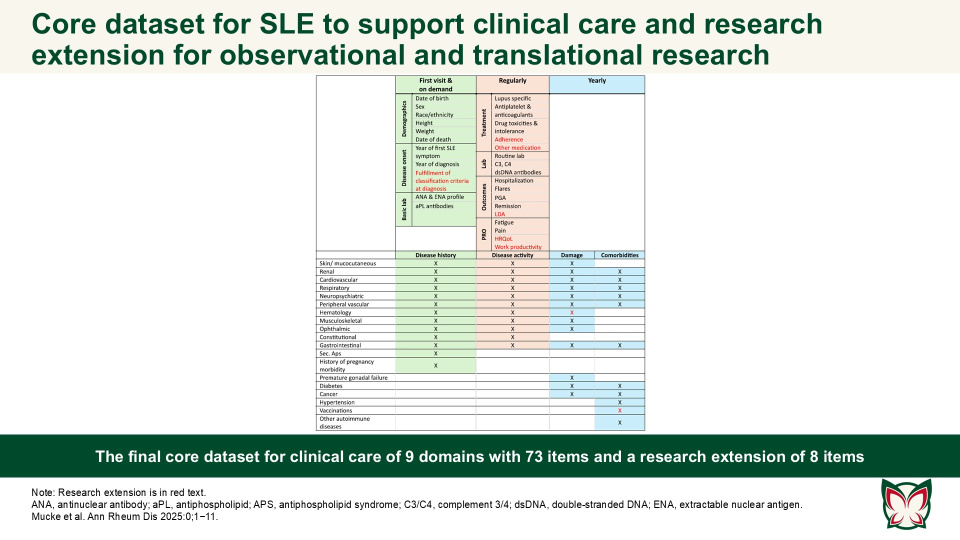
EULAR recommendations for a core dataset to support clinical care and translational and observational research in systemic lupus erythematosus
Ann Rheum Dis 2025:0;1−11 Doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.07.001
The presented clinical core dataset and its research extension are designed to improve SLE patient care and facilitate collaborative research by ensuring the comparability of datasets and cohort descriptions. The aim of this EULAR taskforce by Mucke et al. was to define a core set of essential items for the comprehensive care of SLE patients in clinical practice, with an extension for vital elements required for translational and observational research.
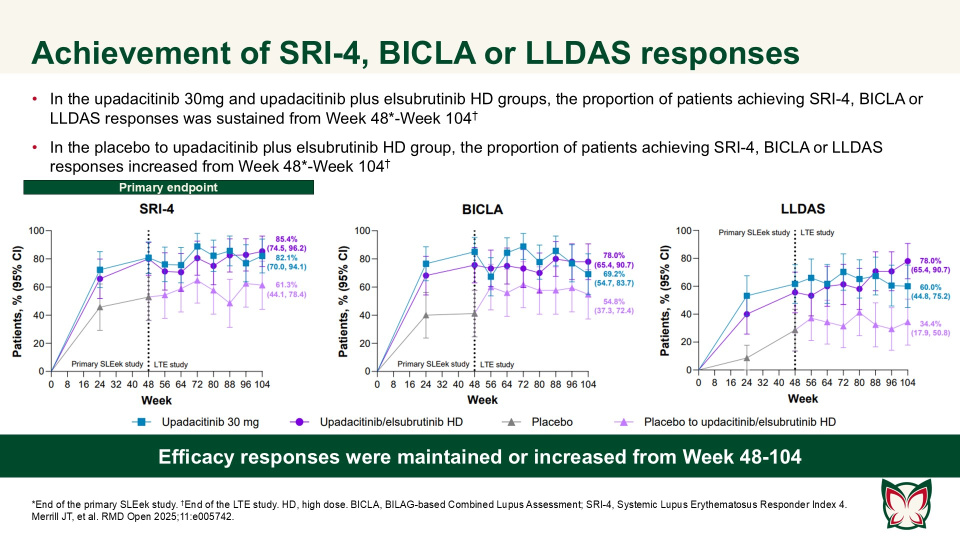
Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: results through 104 weeks in a long-term extension study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005742 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005742
In this long-term extension of the Phase 2 SLEek study, Merrill et al. report that through an additional 56-weeks of treatment, upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib demonstrated sustained or improved efficacy in multiple endpoints in patients with moderately to severely active SLE.
Keywords:
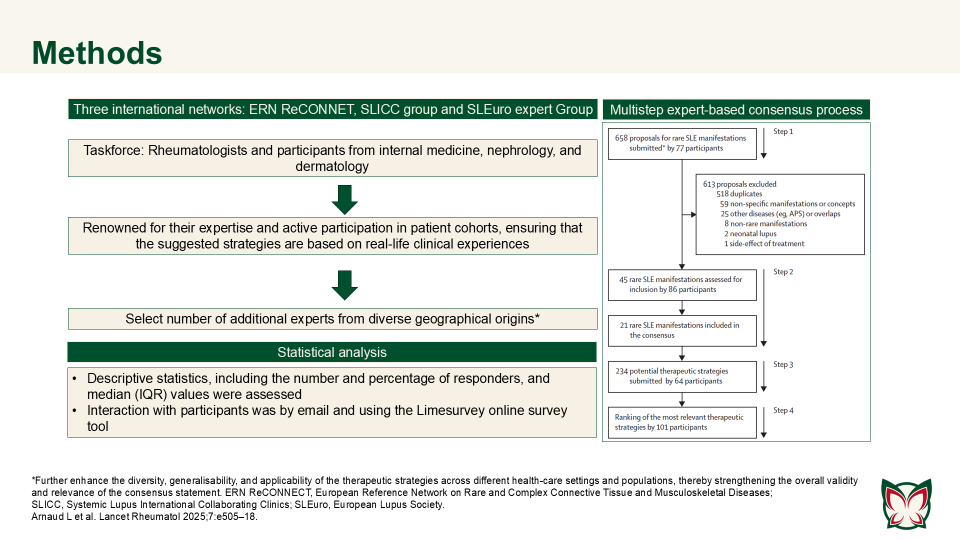
ERN ReCONNET–SLICC–SLEuro expert consensus on the therapeutic management of rare systemic lupus erythematosus manifestations
Lancet Rheumatol 2025;7:e505–18 Doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(25)00063-3
This systematic review highlighted the major gaps in evidence regarding rare SLE manifestations, with many findings dependent on variable methodologies or single reports. Arnard et al. established an international consensus on therapeutic strategies for rare SLE manifestations.
Keywords:
Enhancing systemic lupus erythematosus treatment outcomes with an early initiation of belimumab: insights from a multicenter retrospective study within the first five years
Arthritis Res Ther 2025;27(1):116
Highlighting the importance of early belimumab initiation in SLE, patients with shorter disease duration achieve more substantial improvements in disease activity with early belimumab treatment.
Keywords:
2025 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Guideline for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Guideline Summary
https://rheumatology.org/lupus-guideline#2025-sle-guideline
The ACR have published their summary of the 2025 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Guideline. This updated lupus guideline project is divided into two manuscripts that include renal published (link) and non renal recommendations that are available online in summary now, and the manuscript format due to follow in late 2025.
Keywords:
Domains for inclusion in a novel Treatment Response Measure for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (TRM-SLE): results of a modified Delphi study
Lupus Sci Med. 2025 May 6;12(1):e001484 doi: 10.1136/lupus-2024-001484
Connelly, et al. use Delphi methods to achieve consensus to include eight domains of active disease to define treatment response in a novel Treatment Response Measure for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (TRM-SLE).