Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Efficacy and safety of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: A case series in China
Lancet 2025 Doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(25)01671-X Epub ahead of print
Gao et al. report that allogeneic CAR NK-cell therapy is a potent option for treatment of autoimmune diseases and may address limitations of current autologous CAR T-cell therapy, including manufacturing scale and time, access, safety, and cost. Authors evaluated the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory SLE.
Keywords:
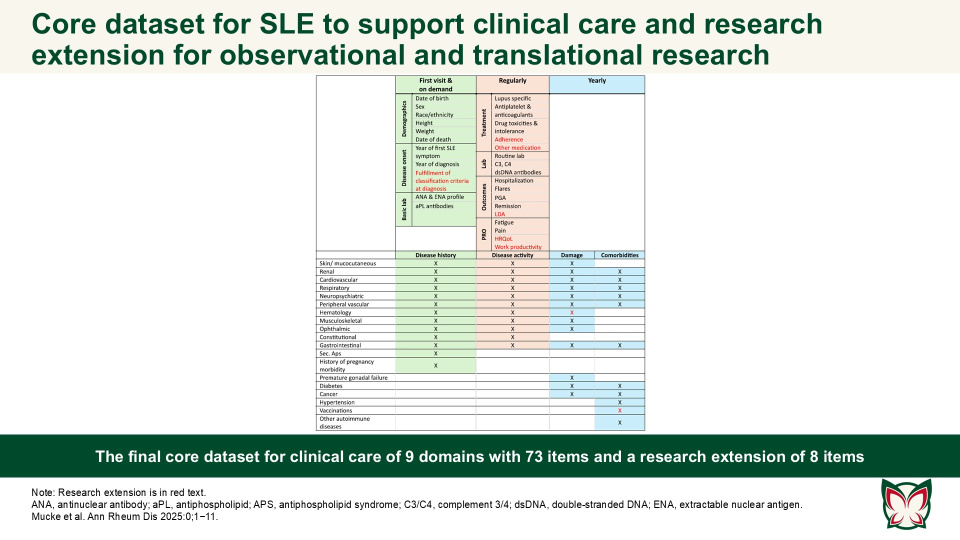
EULAR recommendations for a core dataset to support clinical care and translational and observational research in systemic lupus erythematosus
Ann Rheum Dis 2025:0;1−11 Doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.07.001
The presented clinical core dataset and its research extension are designed to improve SLE patient care and facilitate collaborative research by ensuring the comparability of datasets and cohort descriptions. The aim of this EULAR taskforce by Mucke et al. was to define a core set of essential items for the comprehensive care of SLE patients in clinical practice, with an extension for vital elements required for translational and observational research.
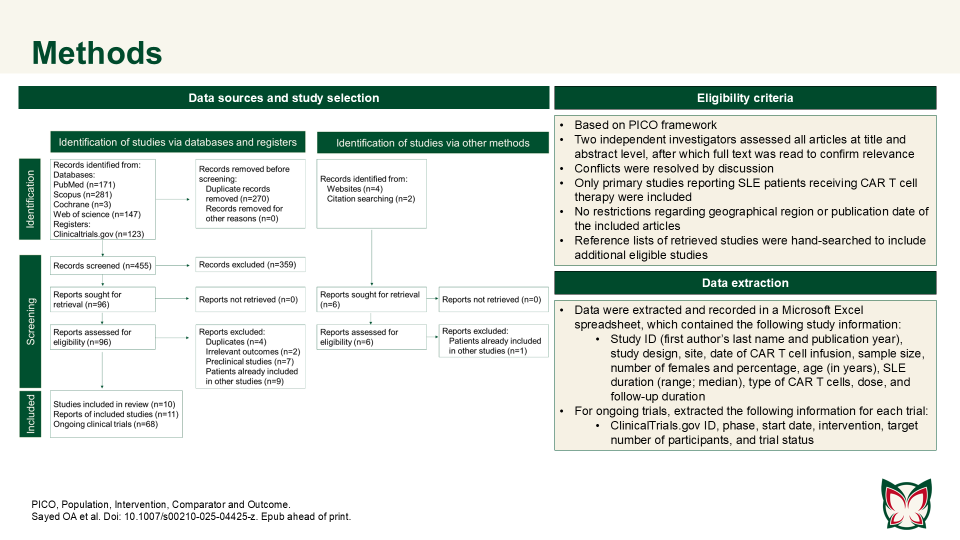
CAR T cell therapy efficacy and safety in SLE: A systematic review and pooled analysis of 47 patients across 10 studies
Doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04425-z
Sayed OA et al. reported that CAR T cell therapy showed promise in refractory SLE, achieving durable remission with manageable toxicity; however further trials are needed to confirm long-term outcomes. Authors consolidated the current evidence on CAR T cell therapy in the treatment of SLE.
BCMA-targeted CAR T cell therapy can effectively induce disease remission in refractory lupus nephritis
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;0:1−9
Hu et al. report that anti-BCMA only CAR T cell can help LN patients safely and effectively, indicating its potential to be a feasible therapeutic strategy in treating autoimmune diseases with abnormal humoral immune responses.
Unsupervised machine learning identifies distinct systemic lupus erythematosus patient endotypes with differential response to belimumab
Rheumatol (Oxford), 2025 DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf215. Epub ahead of print
Depascale et al. used unsupervised machine learning to identify three SLE endotypes based on B cell immunophenotyping and serological profiles. Belimumab was most effective in patients with transitional and naïve B cell enrichment (Cluster 2), where it significantly increased the likelihood of achieving sustained LLDAS and DORIS remission.
Keywords:
Evolution and trajectory of B-cell targeted therapies in rheumatic diseases
Lancet Rheumatol, 2025. Epub ahead of print
Carter et al. review the clinical and mechanistic development of B-cell targeted therapies over the last two decades in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. B-cell depletion depth, repopulation dynamics, and immunogenicity determine long-term efficacy and inform the rationale for emerging
dual-targeted approaches, particularly in systemic lupus erythematosus where belimumab and rituximab combinations show potential to mitigate relapse driven by BAFF.
Opportunities and limitations of B bell depletion approaches in SLE
Nature Review Rheumatol, 2025;21:111–126 DOI: 10.1038/s41584-024-01210-9
Stockfelt et al. reviewed the long-term efficacy and challenges of B cell depletion strategies in SLE. Rituximab, a CD20-targeting monoclonal antibody, has demonstrated efficacy in a subset of patients but remains limited by immunogenicity, residual B cells, and B-cell activating factor (BAFF)-mediated relapse. Newer strategies incorporating CAR T cells, bispecific T cell engagers, and combination therapies aim to enhance B cell depletion and optimise outcomes.
Keywords:
Cenerimod, a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, versus placebo in patients with moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus (CARE): an international, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial
Lancet Rheumatol. 2024. Epub ahead of print. DOI: 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00246-7
Askanase et al. assessed the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of cenerimod in patients with moderate-to-severe SLE. While the primary endpoint of reducing mSLEDAI-2K scores at Month 6 was not achieved, cenerimod 4.0mg showed a significant reduction in disease activity versus placebo. Adverse events, including lymphopenia, were dose-dependent but manageable, and overall treatment was well tolerated.
The 2024 APLAR consensus on the management of lupus nephritis
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases; 28:e70021 DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.70021
Mok et al. provided updated consensus recommendations from APLAR, emphasising evidence-based guidance for managing lupus nephritis in Asian populations. These recommendations consider ethnic, socioeconomic, and pharmacogenetic factors, focusing on treatment regimens, adjunctive therapies, and patient-specific approaches to optimise outcomes.
Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors for the primary prevention of cardiovascular, renal events and safety outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and comorbid type 2 diabetes: A population-based target trial emulation
Arthritis Rheumatol 2024. Epub ahead of print DOI: 10.1002/art.43037
Ma et al. assessed the efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i) in preventing cardiovascular and renal events in patients with both SLE and type 2 diabetes (T2D). SGLT2i use significantly reduced risks for acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, and heart failure, though it increased genital infection risk.