Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
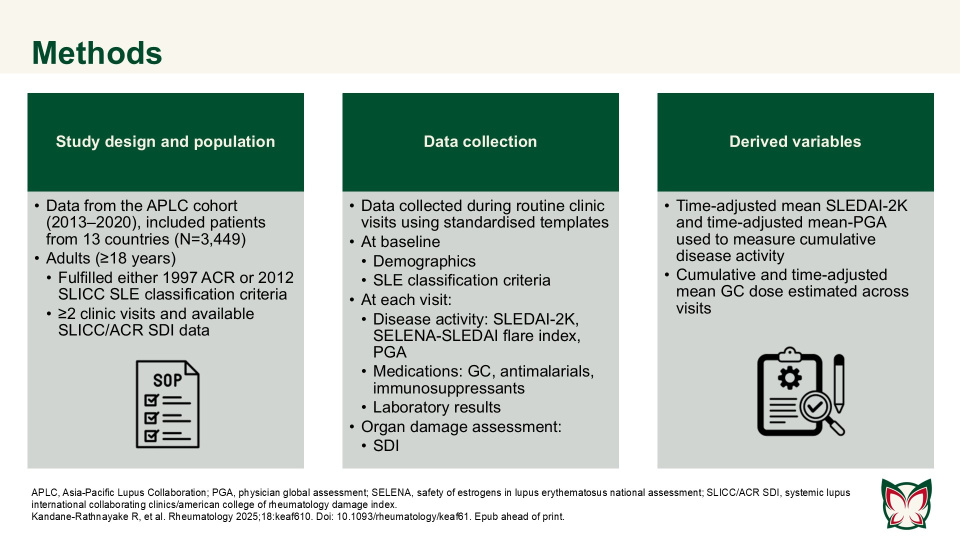
Predictors of damage accrual by organ domain in systemic lupus erythematosus
Rheumatology 2025;18:keaf610 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf610 Epub ahead of print
Kandane-Rathnayake et al. reported that risk factors for individual organ system damage were highly varied in patients with SLE, and not all factors associated with domain-specific damage were captured by summed systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/american college of rheumatology damage index (SLICC/ACR SDI) for overall organ damage.
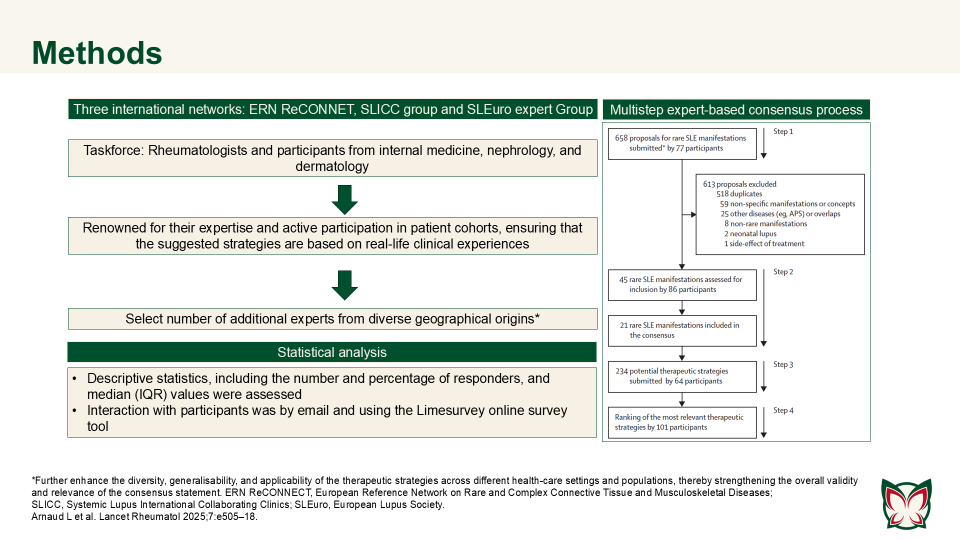
ERN ReCONNET–SLICC–SLEuro expert consensus on the therapeutic management of rare systemic lupus erythematosus manifestations
Lancet Rheumatol 2025;7:e505–18 Doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(25)00063-3
This systematic review highlighted the major gaps in evidence regarding rare SLE manifestations, with many findings dependent on variable methodologies or single reports. Arnard et al. established an international consensus on therapeutic strategies for rare SLE manifestations.
Keywords:
Cenerimod, a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, versus placebo in patients with moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus (CARE): an international, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial
Lancet Rheumatol. 2024. Epub ahead of print. DOI: 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00246-7
Askanase et al. assessed the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of cenerimod in patients with moderate-to-severe SLE. While the primary endpoint of reducing mSLEDAI-2K scores at Month 6 was not achieved, cenerimod 4.0mg showed a significant reduction in disease activity versus placebo. Adverse events, including lymphopenia, were dose-dependent but manageable, and overall treatment was well tolerated.
The 2024 APLAR consensus on the management of lupus nephritis
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases; 28:e70021 DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.70021
Mok et al. provided updated consensus recommendations from APLAR, emphasising evidence-based guidance for managing lupus nephritis in Asian populations. These recommendations consider ethnic, socioeconomic, and pharmacogenetic factors, focusing on treatment regimens, adjunctive therapies, and patient-specific approaches to optimise outcomes.
Burden of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Clinical Practice: Baseline Data from the SLE Prospective Observational Cohort Study (SPOCS) by Interferon Gene Signature
Lupus Sci Med. 2023; 10(2):e001032 DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2023-001032
This study from Arnaud et al described baseline characteristics of SLE patients grouped by disease activity and IFNGS category in the international SPOCS study. IFNGS-high patients were younger at SLE diagnosis, and a baseline SLEDAI-2K score ≥10 was associated with shorter disease duration, more frequent and more severe flares. IFNGS-low patients were more likely to exhibit musculoskeletal and CNS comorbidities than IFNGS-high patients. Continuation of the SPOCS study will allow investigation into how different baseline characteristics affect long-term outcomes in SLE patients.
Keywords:
EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: 2023 Update
Ann Rheum Dis 2023;83(1):15–29 DOI: 10.1136/ard-2023-224762
The objective of this international task force was to update the EULAR recommendations for the management of SLE. The Task Force agreed on 5 overarching principles and 13 recommendations, generating an overall framework for the approach to a patient with SLE. The updated recommendations provide consensus guidance on the management of SLE, combining evidence and expert opinion.
Keywords:
Assessing the Costs of Neuropsychiatric Disease in the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) Cohort using Multistate Modelling
Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2023 doi: 10.1002/acr.25090.
First study to assess the long-term economic burden of neurologic and/or psychiatric (NP) lupus in an international, multi-ethnic inception cohort, concludes that patients with new/ongoing SLE or non-SLE NP events incurred higher direct and indirect costs.
A secondary analysis of the Belimumab International Study in Lupus Nephritis trial examined effects of belimumab on kidney outcomes and preservation of kidney function in patients with lupus nephritis
Kidney Int. 2022;101(2):403-413 doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.08.027
Post-hoc analysis data suggests that the addition of belimumab to standard therapy may be effective in preserving long-term kidney function in patients with lupus nephritis (LN).