Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
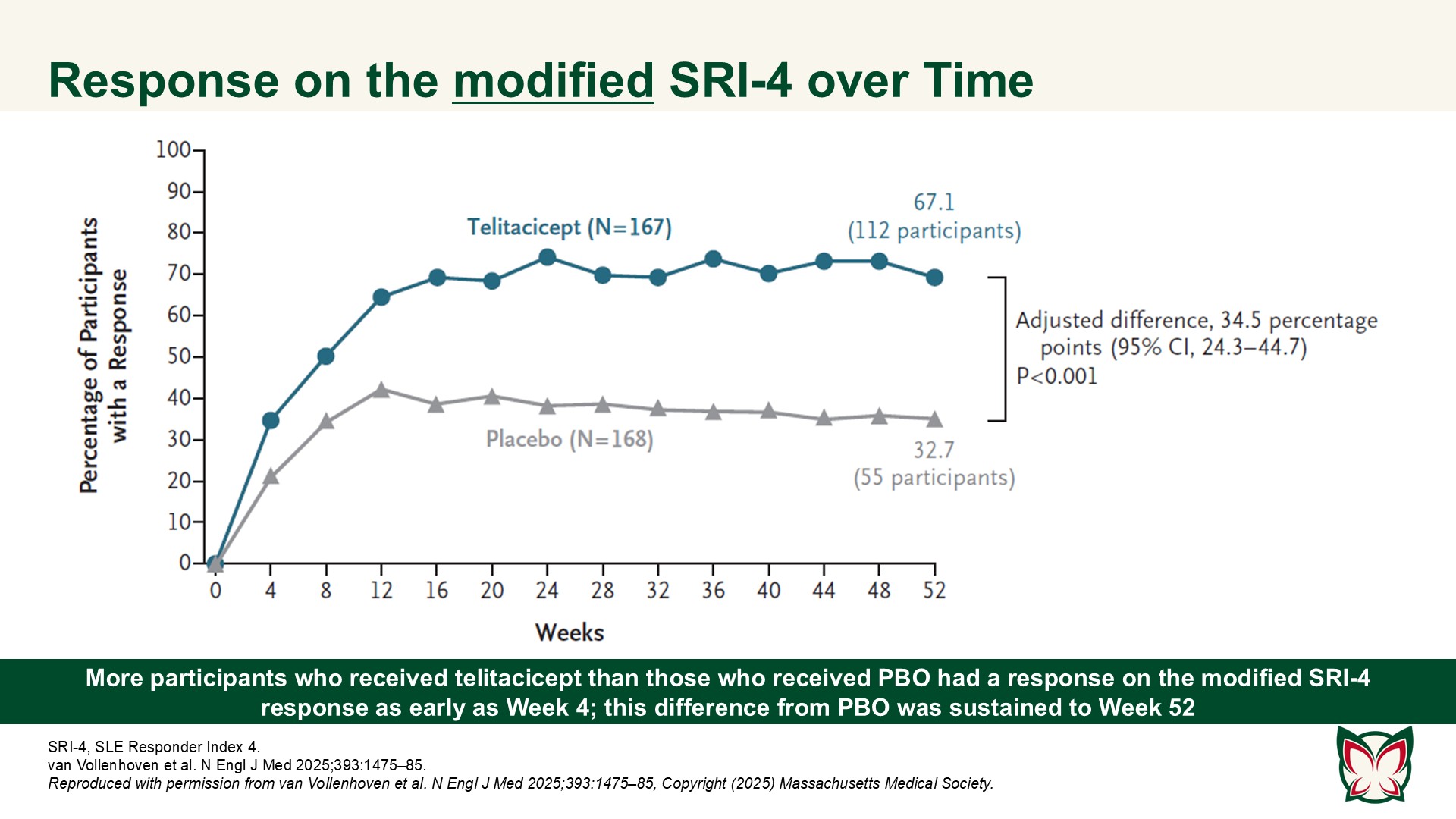
A Phase 3 trial of telitacicept for systemic lupus erythematosus
N Engl J Med 2025;393:1475-85 Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2414719
In this 52-week trial involving participants with active SLE who were receiving background therapy, the incidence of a clinical response was higher with telitacicept than with PBO. van Vollenhoven et al. report efficacy and safety results of a Phase 3 trial of telitacicept at a dose of 160mg weekly as compared with PBO in Chinese persons with active SLE.
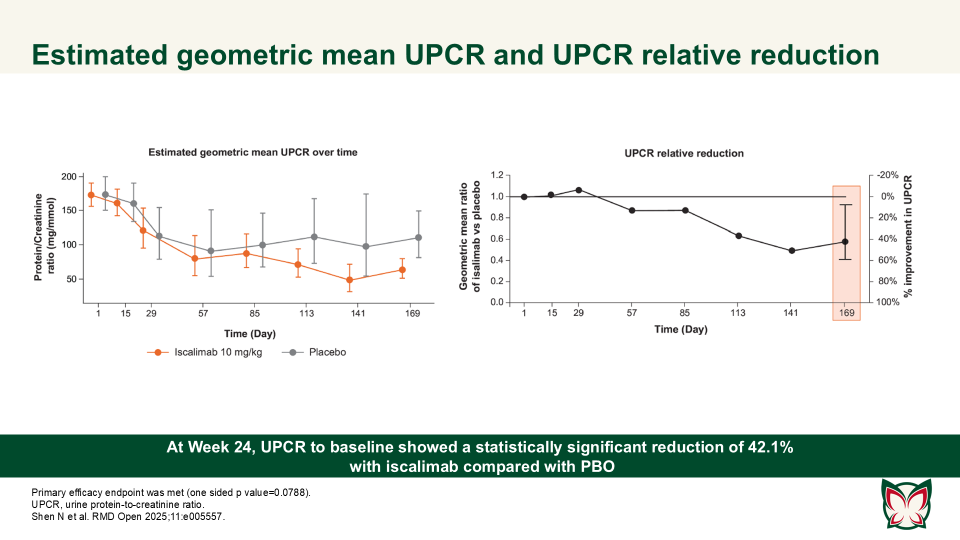
Efficacy, pharmacokinetics and safety of iscalimab (CFZ533) in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase II study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005557 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005557
Shen N et al. report that iscalimab was clinically effective and generally well tolerated; in addition, it was devoid of the thromboembolic risk, characteristic of Fc active anti-CD40L therapies.
Efficacy and safety of obinutuzumab in active lupus nephritis
NEJM, 2025. Epub ahead of print. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2410965
Furie et al. demonstrated that obinutuzumab plus standard therapy significantly improved complete renal response at Wk76 compared with placebo. No unexpected safety signals were identified, though infections and COVID-19-related events were more frequent in the obinutuzumab group.
Belimumab versus telitacicept in sequential treatment after rituximab for refractory lupus nephritis: A real-world multicentre study
Lupus Science & Medicine, 2025;12:e001296 DOI:10.1136/lupus-2024-001296
Chen et al. demonstrated that sequential treatment with belimumab or telitacicept following rituximab (RTX) is a potential therapeutic approach for treating refractory LN. Major AEs included immunoglobin deficiency, respiratory tract infections and urinary tract infections, which are consistent with previous studies.
Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors for the primary prevention of cardiovascular, renal events and safety outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and comorbid type 2 diabetes: A population-based target trial emulation
Arthritis Rheumatol 2024. Epub ahead of print DOI: 10.1002/art.43037
Ma et al. assessed the efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i) in preventing cardiovascular and renal events in patients with both SLE and type 2 diabetes (T2D). SGLT2i use significantly reduced risks for acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, and heart failure, though it increased genital infection risk.
Keywords:
SLESIS-R: an improved score for prediction of serious infection in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus based on the RELESSER prospective cohort
Lupus Sci Med. 2024; 11(1): e001096 DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2023-001096
SLESIS-R may help clinicians make informed decisions on the occurrence of a serious infection in the following year in SLE from four variables: age ≥60 years, previous admission for SLE, previous infection and having received a maximum dose of glucocorticoids ≥30 mg.
Early Infection Risk in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Treated with Rituximab or Belimumab from the British Isles Lupus Assessment Group Biologics Register (BILAG-BR): A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Lancet Rheumatol 2023;5:e284–92 doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00091-7
Data from a large prospective registry (BILAG-BR) highlight that, compared with standard of care, the serious infection risk was similar between rituximab and belimumab.