Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
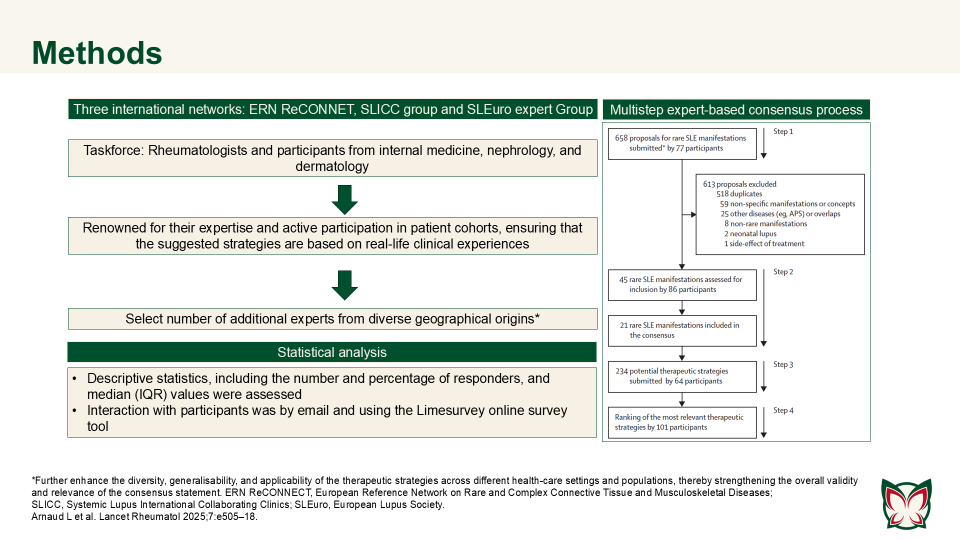
ERN ReCONNET–SLICC–SLEuro expert consensus on the therapeutic management of rare systemic lupus erythematosus manifestations
Lancet Rheumatol 2025;7:e505–18 Doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(25)00063-3
This systematic review highlighted the major gaps in evidence regarding rare SLE manifestations, with many findings dependent on variable methodologies or single reports. Arnard et al. established an international consensus on therapeutic strategies for rare SLE manifestations.
Keywords:
Domains for inclusion in a novel Treatment Response Measure for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (TRM-SLE): results of a modified Delphi study
Lupus Sci Med. 2025 May 6;12(1):e001484 doi: 10.1136/lupus-2024-001484
Connelly, et al. use Delphi methods to achieve consensus to include eight domains of active disease to define treatment response in a novel Treatment Response Measure for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (TRM-SLE).
Efficacy and safety of sequential therapy with subcutaneous belimumab and one cycle of rituximab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: the phase 3, randomised, placebo-controlled BLISS-BELIEVE study
Ann Rheum Dis 2024;0:1–11 DOI 10.1136/ard-2024-225686.
Aranow et al. evaluated the efficacy and safety of combining subcutaneous belimumab with one cycle of rituximab in SLE. Sequential therapy did not show a statistically significant improvement in disease control over belimumab monotherapy, but did achieve nominally better reductions in disease activity markers.
Keywords:
Mycophenolate mofetil withdrawal in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial
Lancet Rheumatol 224;6(3):e168–77 DOI 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00320-X
Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) withdrawal was not significantly inferior to MMF maintenance through Week 60 in patients with SLE that had been treated with MMF for ≥1 year.
Keywords:
Association Between Severe Nonadherence to Hydroxychloroquine and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Flares, Damage, and Mortality in 660 Patients From the SLICC Inception Cohort
Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75(12):2195–2206 DOI: 10.1002/art.42645
n this study, severe nonadherence to hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was independently associated with the risk of SLE flare in the following year, early damage and 5-year mortality.
Keywords:
Machine Learning Identifies Clusters of Longitudinal Autoantibody Profiles Predictive of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Outcomes
Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82(7):927–36 doi 10.1136/ard-2022-223808
Choi, et al. used machine clustering techniques to divide SLE patients into four distinct clusters. This could potentially be used to predict future clinical outcomes, and as benchmarks to study other SLE-related outcomes.
Keywords:
Assessing the Costs of Neuropsychiatric Disease in the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) Cohort using Multistate Modelling
Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2023 doi: 10.1002/acr.25090.
First study to assess the long-term economic burden of neurologic and/or psychiatric (NP) lupus in an international, multi-ethnic inception cohort, concludes that patients with new/ongoing SLE or non-SLE NP events incurred higher direct and indirect costs.