Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
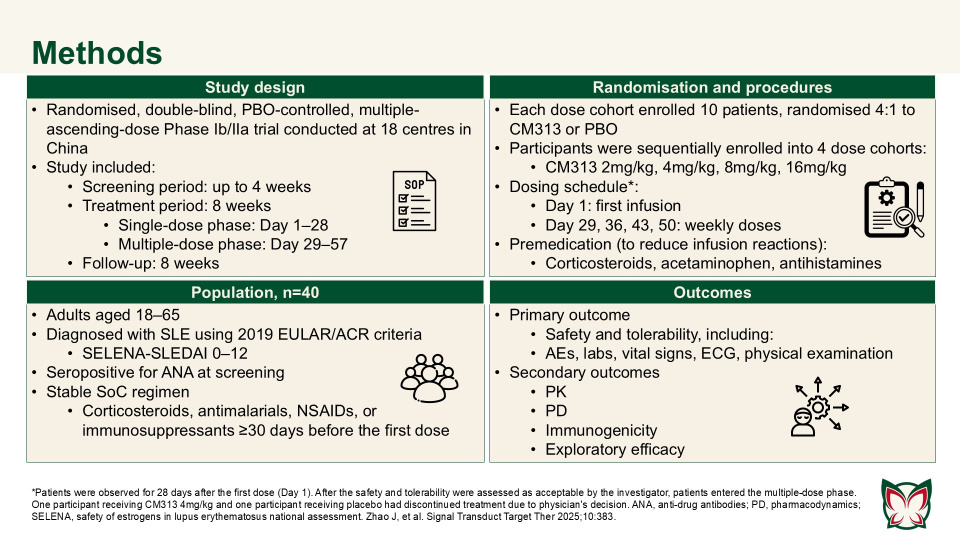
Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody CM313 for systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase Ib/IIa trial
Signal Transduct Target Ther 2025;10:383 Doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02487-2
Zhao et al. showed that CM313 was well tolerated in adult patients with SLE at doses of 2–16mg/kg and showed encouraging pharmacodynamic effects and preliminary efficacy at doses of 8 and 16 mg/kg QW. CM313 also produced dose-dependent and clinically meaningful improvements in key serological biomarkers of SLE.
Efficacy and safety of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: A case series in China
Lancet 2025 Doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(25)01671-X Epub ahead of print
Gao et al. report that allogeneic CAR NK-cell therapy is a potent option for treatment of autoimmune diseases and may address limitations of current autologous CAR T-cell therapy, including manufacturing scale and time, access, safety, and cost. Authors evaluated the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory SLE.
Keywords:
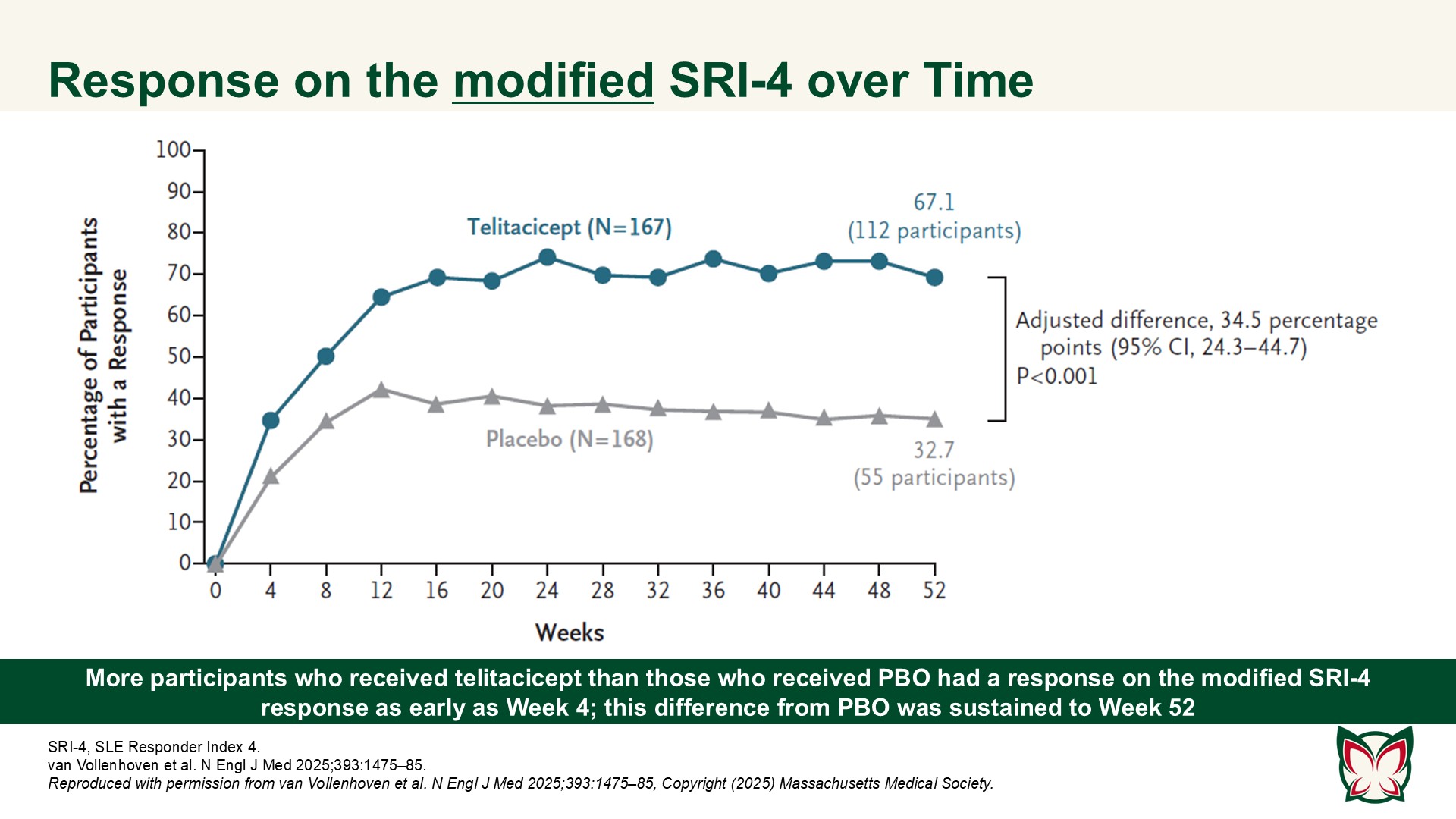
A Phase 3 trial of telitacicept for systemic lupus erythematosus
N Engl J Med 2025;393:1475-85 Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2414719
In this 52-week trial involving participants with active SLE who were receiving background therapy, the incidence of a clinical response was higher with telitacicept than with PBO. van Vollenhoven et al. report efficacy and safety results of a Phase 3 trial of telitacicept at a dose of 160mg weekly as compared with PBO in Chinese persons with active SLE.
Secukinumab in active lupus nephritis: Results from Phase III, randomised, placebo controlled study (SELUNE) and open-label extension study
Rheumatology 2025 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf536 Epub ahead of print
Secukinumab did not demonstrate superior efficacy over PBO in patients with active LN; secukinumab was well-tolerated with no new or unexpected safety signals detected. A Phase-III core study (SELUNE) and an extension study, were conducted by Zhao et al. to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SC secukinumab 300mg compared with PBO, in combination with the SoC, in patients with active LN.
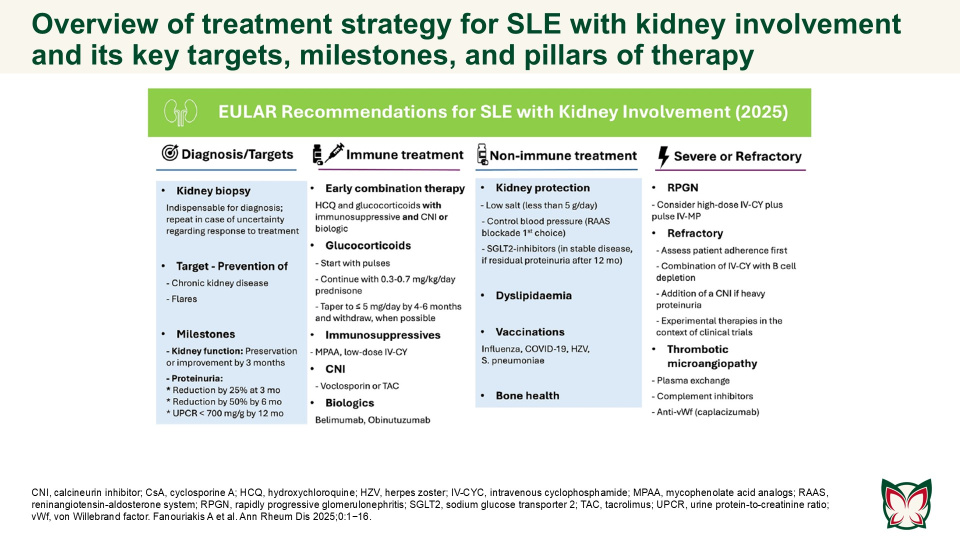
EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus with kidney involvement: 2025 update
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;0:1−16 Doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.09.007
The updated EULAR recommendations provide evidence- and expert-based consensus on the management of SLE with kidney involvement, adjusted for severity, and taking into consideration long-term efficacy, safety, cost, and local availability of drugs. Fanouriakis A et al. updated the 2019 EULAR/ ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of SLE with kidney involvement, taking into consideration emerging evidence and recent developments in the field.
Keywords:
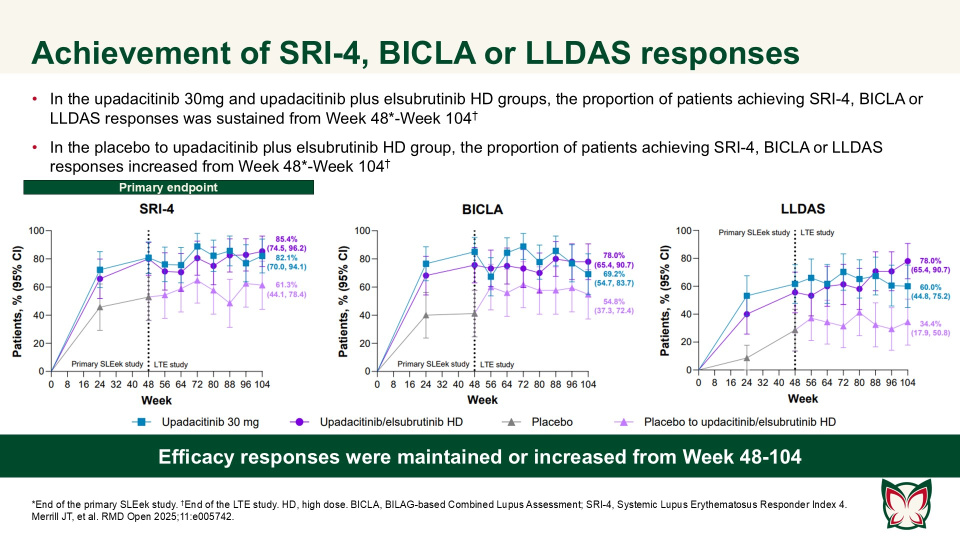
Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: results through 104 weeks in a long-term extension study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005742 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005742
In this long-term extension of the Phase 2 SLEek study, Merrill et al. report that through an additional 56-weeks of treatment, upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib demonstrated sustained or improved efficacy in multiple endpoints in patients with moderately to severely active SLE.
Keywords:
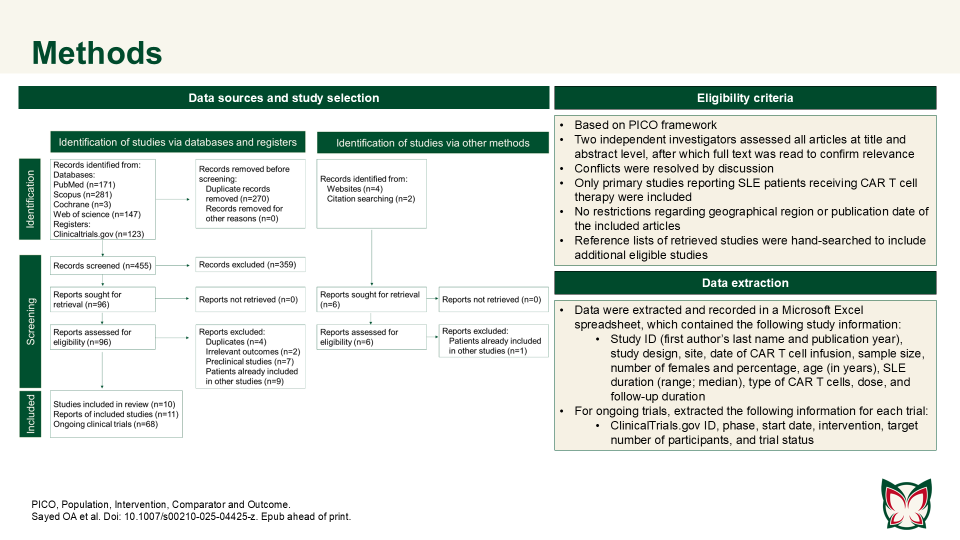
CAR T cell therapy efficacy and safety in SLE: A systematic review and pooled analysis of 47 patients across 10 studies
Doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04425-z
Sayed OA et al. reported that CAR T cell therapy showed promise in refractory SLE, achieving durable remission with manageable toxicity; however further trials are needed to confirm long-term outcomes. Authors consolidated the current evidence on CAR T cell therapy in the treatment of SLE.
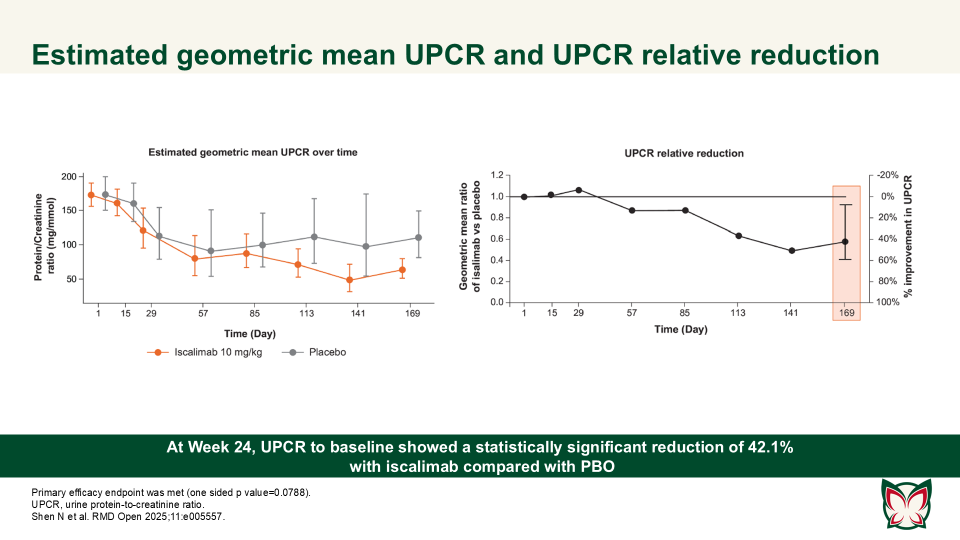
Efficacy, pharmacokinetics and safety of iscalimab (CFZ533) in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase II study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005557 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005557
Shen N et al. report that iscalimab was clinically effective and generally well tolerated; in addition, it was devoid of the thromboembolic risk, characteristic of Fc active anti-CD40L therapies.
BCMA-targeted CAR T cell therapy can effectively induce disease remission in refractory lupus nephritis
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;0:1−9
Hu et al. report that anti-BCMA only CAR T cell can help LN patients safely and effectively, indicating its potential to be a feasible therapeutic strategy in treating autoimmune diseases with abnormal humoral immune responses.
Effect of long-term voclosporin treatment on renal histology in patients with active lupus nephritis with repeat renal biopsies
Arthritis & Rheumatology 2025; 0:1–7 doi: 10.1002/art.43209
Exposure to voclosporin for a median of 18 months was not associated with onset or progression of nephrotoxicity based on evaluation of histologic compartments and vascular lesions. Rovin et al. characterised the impact of voclosporin on kidney histology in patients with LN who had protocolized repeat kidney biopsies in the AURORA clinical trials.