Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
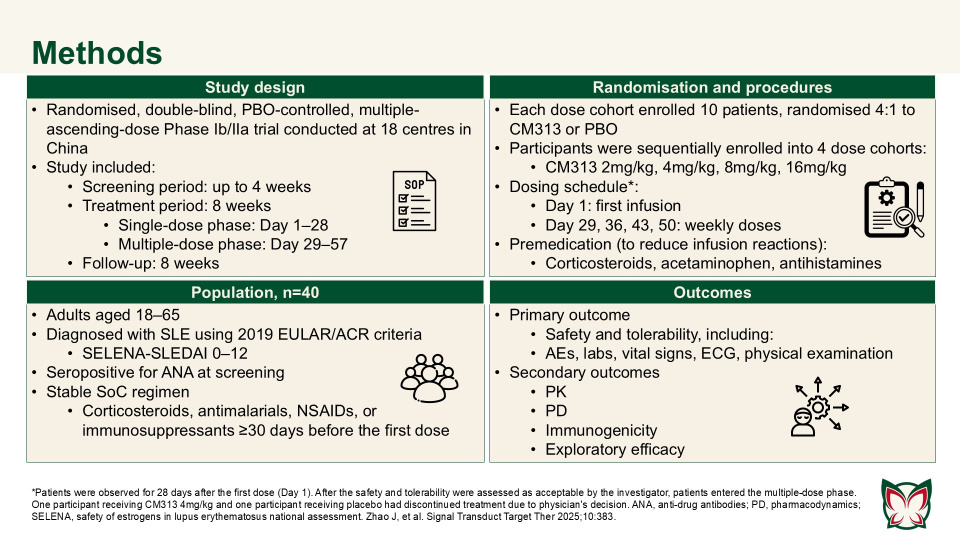
Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody CM313 for systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase Ib/IIa trial
Signal Transduct Target Ther 2025;10:383 Doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02487-2
Zhao et al. showed that CM313 was well tolerated in adult patients with SLE at doses of 2–16mg/kg and showed encouraging pharmacodynamic effects and preliminary efficacy at doses of 8 and 16 mg/kg QW. CM313 also produced dose-dependent and clinically meaningful improvements in key serological biomarkers of SLE.
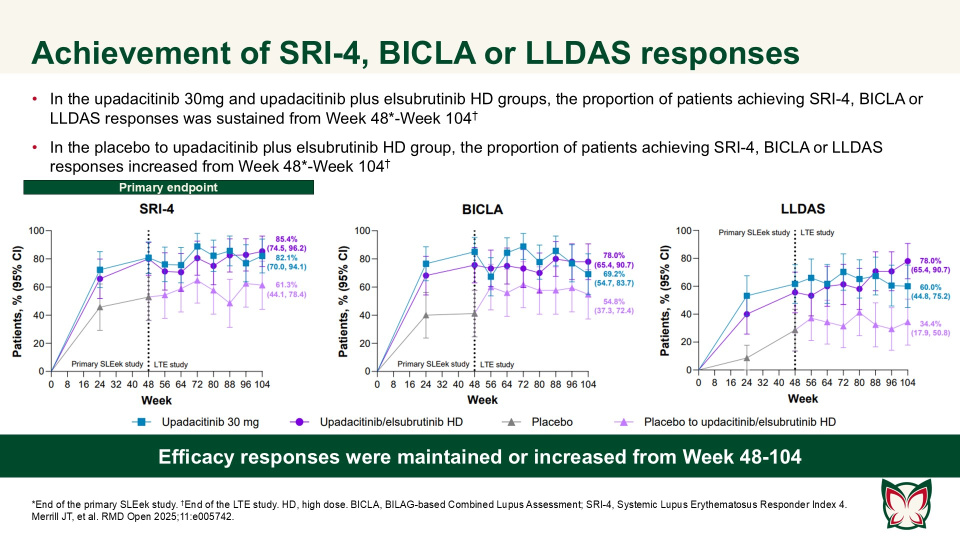
Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: results through 104 weeks in a long-term extension study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005742 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005742
In this long-term extension of the Phase 2 SLEek study, Merrill et al. report that through an additional 56-weeks of treatment, upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib demonstrated sustained or improved efficacy in multiple endpoints in patients with moderately to severely active SLE.
Keywords:
LLDAS and remission attainment with anifrolumab treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the TULIP and long-term extension randomised controlled trials
Ann Rheum Dis. 2025:S0003-496700071-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.01.016. Epub ahead of print
Morand et al. conducted a post-hoc analysis of the phase III TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials and their long-term extension, including 369 patients with moderate to severe SLE, to evaluate the long-term impact of anifrolumab on attainment of LLDAS and DORIS-defined remission. The results demonstrated that anifrolumab significantly improved the likelihood, speed, and duration of LLDAS and DORIS remission versus placebo over 4 years, with benefits sustained throughout the treatment period.
Keywords:
Evolution and trajectory of B-cell targeted therapies in rheumatic diseases
Lancet Rheumatol, 2025. Epub ahead of print
Carter et al. review the clinical and mechanistic development of B-cell targeted therapies over the last two decades in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. B-cell depletion depth, repopulation dynamics, and immunogenicity determine long-term efficacy and inform the rationale for emerging
dual-targeted approaches, particularly in systemic lupus erythematosus where belimumab and rituximab combinations show potential to mitigate relapse driven by BAFF.
Opportunities and limitations of B bell depletion approaches in SLE
Nature Review Rheumatol, 2025;21:111–126 DOI: 10.1038/s41584-024-01210-9
Stockfelt et al. reviewed the long-term efficacy and challenges of B cell depletion strategies in SLE. Rituximab, a CD20-targeting monoclonal antibody, has demonstrated efficacy in a subset of patients but remains limited by immunogenicity, residual B cells, and B-cell activating factor (BAFF)-mediated relapse. Newer strategies incorporating CAR T cells, bispecific T cell engagers, and combination therapies aim to enhance B cell depletion and optimise outcomes.