Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Low-dose belimumab reduced risk of flares in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Ann Rheum Dis 2025 Doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.10.010. Epub ahead of print
Sun et al. provides the first RCT evidence that low-dose belimumab reduces flares in patients with SLE with low-grade disease activity. Authors evaluated the efficacy of low-dose belimumab for disease flare prevention in Chinese patients with low-grade SLE (SELENA-SLEDAI ≤6).
Keywords:
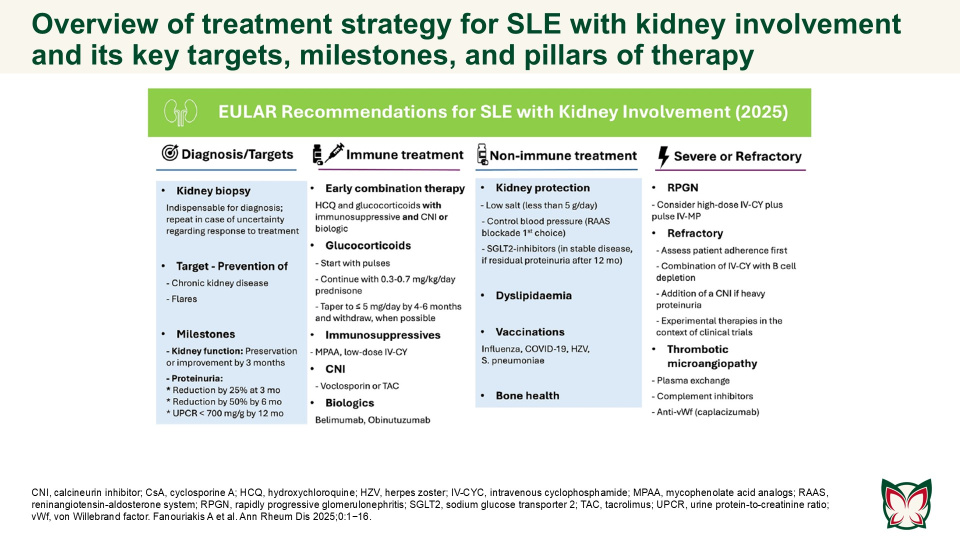
EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus with kidney involvement: 2025 update
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;0:1−16 Doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.09.007
The updated EULAR recommendations provide evidence- and expert-based consensus on the management of SLE with kidney involvement, adjusted for severity, and taking into consideration long-term efficacy, safety, cost, and local availability of drugs. Fanouriakis A et al. updated the 2019 EULAR/ ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of SLE with kidney involvement, taking into consideration emerging evidence and recent developments in the field.
Keywords:
Secukinumab in active lupus nephritis: Results from Phase III, randomised, placebo controlled study (SELUNE) and open-label extension study
Rheumatology 2025 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf536 Epub ahead of print
Secukinumab did not demonstrate superior efficacy over PBO in patients with active LN; secukinumab was well-tolerated with no new or unexpected safety signals detected. A Phase-III core study (SELUNE) and an extension study, were conducted by Zhao et al. to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SC secukinumab 300mg compared with PBO, in combination with the SoC, in patients with active LN.
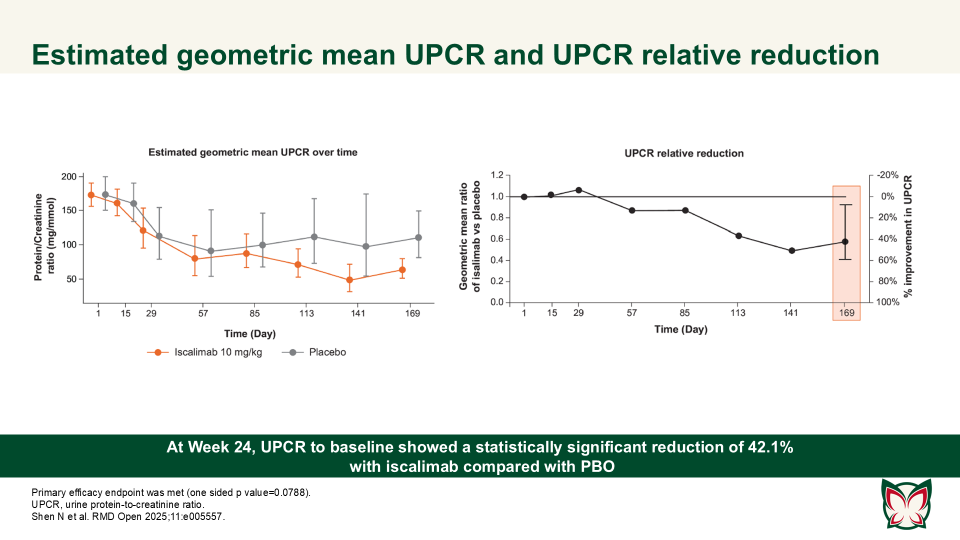
Efficacy, pharmacokinetics and safety of iscalimab (CFZ533) in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase II study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005557 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005557
Shen N et al. report that iscalimab was clinically effective and generally well tolerated; in addition, it was devoid of the thromboembolic risk, characteristic of Fc active anti-CD40L therapies.
BCMA-targeted CAR T cell therapy can effectively induce disease remission in refractory lupus nephritis
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;0:1−9
Hu et al. report that anti-BCMA only CAR T cell can help LN patients safely and effectively, indicating its potential to be a feasible therapeutic strategy in treating autoimmune diseases with abnormal humoral immune responses.
Effect of long-term voclosporin treatment on renal histology in patients with active lupus nephritis with repeat renal biopsies
Arthritis & Rheumatology 2025; 0:1–7 doi: 10.1002/art.43209
Exposure to voclosporin for a median of 18 months was not associated with onset or progression of nephrotoxicity based on evaluation of histologic compartments and vascular lesions. Rovin et al. characterised the impact of voclosporin on kidney histology in patients with LN who had protocolized repeat kidney biopsies in the AURORA clinical trials.
Keywords:
Efficacy and safety of obinutuzumab in active lupus nephritis
NEJM, 2025. Epub ahead of print. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2410965
Furie et al. demonstrated that obinutuzumab plus standard therapy significantly improved complete renal response at Wk76 compared with placebo. No unexpected safety signals were identified, though infections and COVID-19-related events were more frequent in the obinutuzumab group.
Belimumab versus telitacicept in sequential treatment after rituximab for refractory lupus nephritis: A real-world multicentre study
Lupus Science & Medicine, 2025;12:e001296 DOI:10.1136/lupus-2024-001296
Chen et al. demonstrated that sequential treatment with belimumab or telitacicept following rituximab (RTX) is a potential therapeutic approach for treating refractory LN. Major AEs included immunoglobin deficiency, respiratory tract infections and urinary tract infections, which are consistent with previous studies.
Comparison of a voclosporin-based triple immunosuppressive therapy to high-dose glucocorticoid-based immunosuppressive therapy: A propensity analysis of the AURA-LV and AURORA 1 studies and ALMS
Lupus Science & Medicine 2024;11:e001319 DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2024-001319
Dall’Era et al. conducted a propensity analysis to compare voclosporin-based triple immunosuppressive therapy with high-dose GC-based regimens for active LN. Voclosporin showed fewer AEs, improved safety, and significantly reduced proteinuria over six months, suggesting a superior risk-benefit profile for patients with lupus nephritis.
Keywords:
The 2024 APLAR consensus on the management of lupus nephritis
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases; 28:e70021 DOI: 10.1111/1756-185X.70021
Mok et al. provided updated consensus recommendations from APLAR, emphasising evidence-based guidance for managing lupus nephritis in Asian populations. These recommendations consider ethnic, socioeconomic, and pharmacogenetic factors, focusing on treatment regimens, adjunctive therapies, and patient-specific approaches to optimise outcomes.