Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
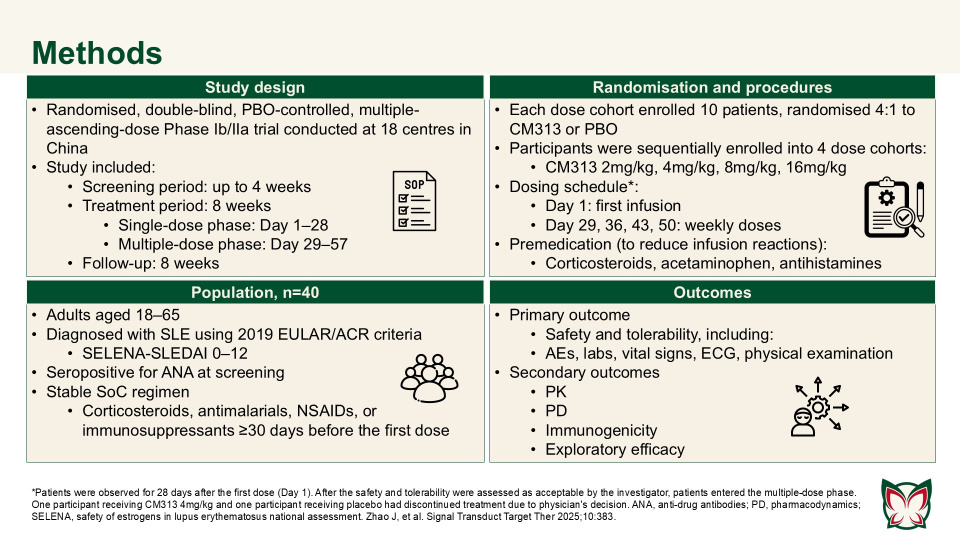
Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody CM313 for systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase Ib/IIa trial
Signal Transduct Target Ther 2025;10:383 Doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02487-2
Zhao et al. showed that CM313 was well tolerated in adult patients with SLE at doses of 2–16mg/kg and showed encouraging pharmacodynamic effects and preliminary efficacy at doses of 8 and 16 mg/kg QW. CM313 also produced dose-dependent and clinically meaningful improvements in key serological biomarkers of SLE.
Opportunities and limitations of B bell depletion approaches in SLE
Nature Review Rheumatol, 2025;21:111–126 DOI: 10.1038/s41584-024-01210-9
Stockfelt et al. reviewed the long-term efficacy and challenges of B cell depletion strategies in SLE. Rituximab, a CD20-targeting monoclonal antibody, has demonstrated efficacy in a subset of patients but remains limited by immunogenicity, residual B cells, and B-cell activating factor (BAFF)-mediated relapse. Newer strategies incorporating CAR T cells, bispecific T cell engagers, and combination therapies aim to enhance B cell depletion and optimise outcomes.
Keywords:
Efficacy and safety of obinutuzumab in active lupus nephritis
NEJM, 2025. Epub ahead of print. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2410965
Furie et al. demonstrated that obinutuzumab plus standard therapy significantly improved complete renal response at Wk76 compared with placebo. No unexpected safety signals were identified, though infections and COVID-19-related events were more frequent in the obinutuzumab group.
Trial of Anti-BDCA2 Antibody Litifilimab for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
N Engl J Med. 2022;387(10):894–904 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2118025
Phase 2 study, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, shows that litifilimab is associated with a greater reduction from baseline in the number of swollen and tender joints than placebo, over a period of 24 weeks.
Phase II randomised trial of type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in patients with active lupus nephritis
Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(4):496–506 doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221478
Despite not meeting the primary endpoint, this Phase II trial of anifrolumab in patients with active lupus nephritis (LN) demonstrates that anifrolumab IR is associated with numerical improvements over placebo across endpoints – including complete renal response – in patients with active LN.
Keywords:
A secondary analysis of the Belimumab International Study in Lupus Nephritis trial examined effects of belimumab on kidney outcomes and preservation of kidney function in patients with lupus nephritis
Kidney Int. 2022;101(2):403-413 doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.08.027
Post-hoc analysis data suggests that the addition of belimumab to standard therapy may be effective in preserving long-term kidney function in patients with lupus nephritis (LN).
Efficacy of anifrolumab across organ domains in patients with moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus: a post-hoc analysis of pooled data from the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials
Lancet Rheumatol. Published online February 3, 2022
Across two pivotal phase 3 trials (TULIP-1 and TULIP-2), anifrolumab treatment improved systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease activity across multiple organ domains, compared with placebo.