Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
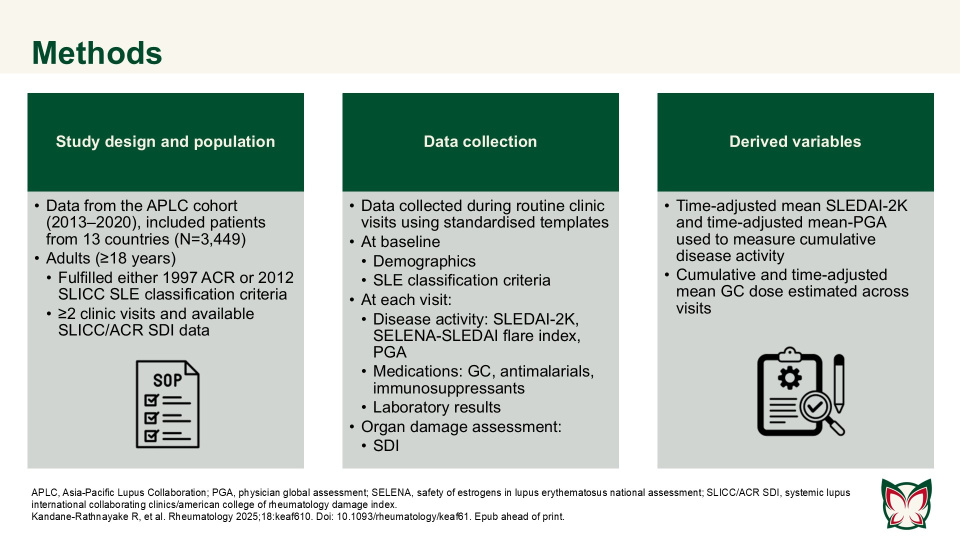
Predictors of damage accrual by organ domain in systemic lupus erythematosus
Rheumatology 2025;18:keaf610 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf610 Epub ahead of print
Kandane-Rathnayake et al. reported that risk factors for individual organ system damage were highly varied in patients with SLE, and not all factors associated with domain-specific damage were captured by summed systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/american college of rheumatology damage index (SLICC/ACR SDI) for overall organ damage.
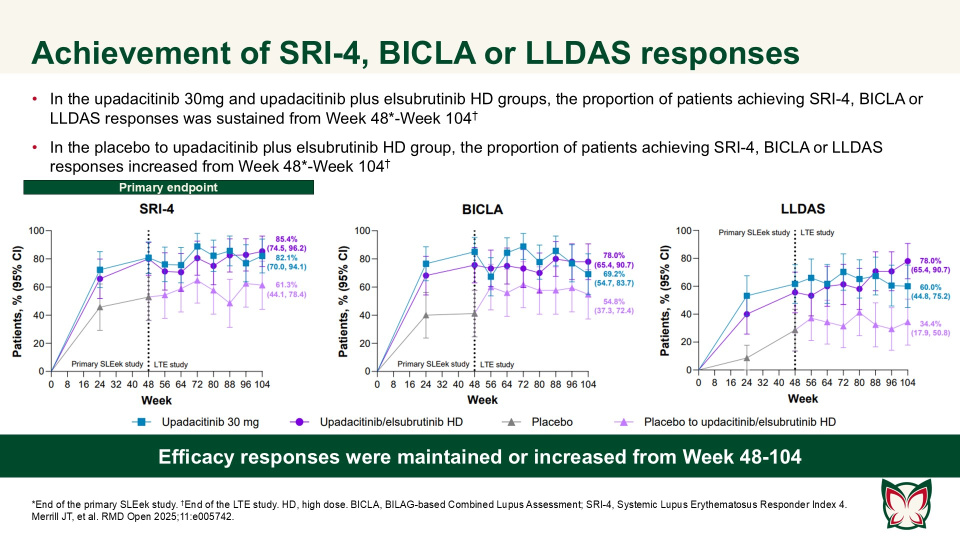
Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: results through 104 weeks in a long-term extension study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005742 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005742
In this long-term extension of the Phase 2 SLEek study, Merrill et al. report that through an additional 56-weeks of treatment, upadacitinib as monotherapy or combined with elsubrutinib demonstrated sustained or improved efficacy in multiple endpoints in patients with moderately to severely active SLE.
Keywords:
Effect of iberdomide on cutaneous manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized phase 2 clinical trial
JAAD. 2024. Epub ahead of print DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2024.09.074
Werth et al. demonstrated that iberdomide significantly improved cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) outcomes, particularly in subacute and chronic CLE patients, by reducing Cutaneous Lupus Area and Severity Index Activity (CLASI-A) scores. The study showed continued efficacy through 24 weeks, with the 0.45 mg dose providing the greatest improvement in patients with severe baseline scores, and iberdomide was well-tolerated over 104 weeks.
Keywords:
Attainment of EULAR/ERA-EDTA targets of therapy with current immunosuppressive regimens and adjustments in treatment: a multicentre, real-life observational study
RMD Open 2024;10:e004437 DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004437
Pappa et al. explored the achievement of EULAR/ERA-EDTA targets in lupus nephritis patients receiving standard immunosuppressive therapy. Two-thirds of the cohort achieved target responses by 12 months, but 20% required therapy modifications due to suboptimal outcomes.
Keywords:
CD19 CAR T-Cell therapy in autoimmune disease - A case series with follow-up
N Engl J Med 2024;390(8):687–700 DOI 10.1056/NEJMoa2308917
In this case series by Müller, et al., eight patients who received a CD19 CAR T-cell infusion achieved Definition of Remission in SLE (DORIS) remission, Lupus Low Disease Activity State and a SLEDAI 2K score of 0 at 6 months post-infusion. Long-term follow-up through 24 months showed that SLE disease activity remained absent
in all eight patients.
Keywords:
Easy-BILAG: a new tool for simplified recording of SLE disease activity using BILAG-2004 index
Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022. Epub ahead of print doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab883
Easy-BILAG is a high-accuracy, time-efficient tool for recording BILAG-2004 disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Disease activity measurements in SLE are necessary for optimal patient care, treat-to-target approaches and clinical guidelines. However, administrative burden and potential frequency of errors with the current comprehensive disease activity instrument (BILAG-2004) limits its use in routine practice.