Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Secukinumab in active lupus nephritis: Results from Phase III, randomised, placebo controlled study (SELUNE) and open-label extension study
Rheumatology 2025 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf536 Epub ahead of print
Secukinumab did not demonstrate superior efficacy over PBO in patients with active LN; secukinumab was well-tolerated with no new or unexpected safety signals detected. A Phase-III core study (SELUNE) and an extension study, were conducted by Zhao et al. to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SC secukinumab 300mg compared with PBO, in combination with the SoC, in patients with active LN.
CAR T cell therapy efficacy and safety in SLE: A systematic review and pooled analysis of 47 patients across 10 studies
Doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04425-z
Sayed OA et al. reported that CAR T cell therapy showed promise in refractory SLE, achieving durable remission with manageable toxicity; however further trials are needed to confirm long-term outcomes. Authors consolidated the current evidence on CAR T cell therapy in the treatment of SLE.
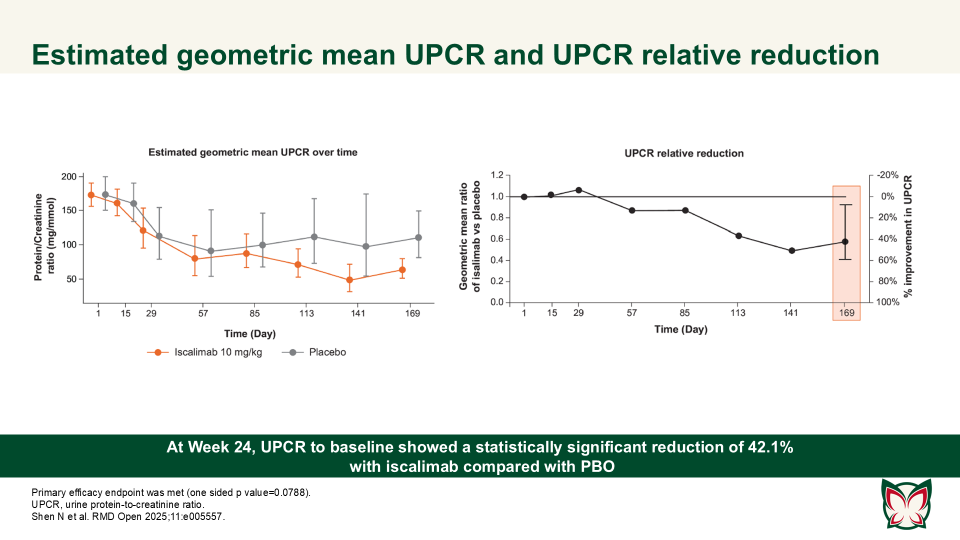
Efficacy, pharmacokinetics and safety of iscalimab (CFZ533) in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase II study
RMD Open 2025;11:e005557 Doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005557
Shen N et al. report that iscalimab was clinically effective and generally well tolerated; in addition, it was devoid of the thromboembolic risk, characteristic of Fc active anti-CD40L therapies.
Effect of long-term voclosporin treatment on renal histology in patients with active lupus nephritis with repeat renal biopsies
Arthritis & Rheumatology 2025; 0:1–7 doi: 10.1002/art.43209
Exposure to voclosporin for a median of 18 months was not associated with onset or progression of nephrotoxicity based on evaluation of histologic compartments and vascular lesions. Rovin et al. characterised the impact of voclosporin on kidney histology in patients with LN who had protocolized repeat kidney biopsies in the AURORA clinical trials.
Keywords:
2025 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Guideline for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Guideline Summary
https://rheumatology.org/lupus-guideline#2025-sle-guideline
The ACR have published their summary of the 2025 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Guideline. This updated lupus guideline project is divided into two manuscripts that include renal published (link) and non renal recommendations that are available online in summary now, and the manuscript format due to follow in late 2025.
Keywords:
Efficacy and safety of obinutuzumab in active lupus nephritis
NEJM, 2025. Epub ahead of print. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2410965
Furie et al. demonstrated that obinutuzumab plus standard therapy significantly improved complete renal response at Wk76 compared with placebo. No unexpected safety signals were identified, though infections and COVID-19-related events were more frequent in the obinutuzumab group.
Belimumab versus telitacicept in sequential treatment after rituximab for refractory lupus nephritis: A real-world multicentre study
Lupus Science & Medicine, 2025;12:e001296 DOI:10.1136/lupus-2024-001296
Chen et al. demonstrated that sequential treatment with belimumab or telitacicept following rituximab (RTX) is a potential therapeutic approach for treating refractory LN. Major AEs included immunoglobin deficiency, respiratory tract infections and urinary tract infections, which are consistent with previous studies.
Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors for the primary prevention of cardiovascular, renal events and safety outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and comorbid type 2 diabetes: A population-based target trial emulation
Arthritis Rheumatol 2024. Epub ahead of print DOI: 10.1002/art.43037
Ma et al. assessed the efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) compared with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i) in preventing cardiovascular and renal events in patients with both SLE and type 2 diabetes (T2D). SGLT2i use significantly reduced risks for acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, and heart failure, though it increased genital infection risk.
Keywords:
Attainment of EULAR/ERA-EDTA targets of therapy with current immunosuppressive regimens and adjustments in treatment: a multicentre, real-life observational study
RMD Open 2024;10:e004437 DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004437
Pappa et al. explored the achievement of EULAR/ERA-EDTA targets in lupus nephritis patients receiving standard immunosuppressive therapy. Two-thirds of the cohort achieved target responses by 12 months, but 20% required therapy modifications due to suboptimal outcomes.
Keywords:
Immunosuppressives discontinuation after renal response in lupus nephritis: predictors of flares, time to withdrawal and long-term outcomes
Rheumatol 2024 DOI 10.1093/rheumatology/keae381 Epub ahead of print
This study by Panagiotopoulos, et al. showed that an early complete renal response achievement, persistent hydroxychloroquine use, and the maintenance of optimal low disease activity during follow-up in immunosuppressive (IS) tapering and discontinuation are fundamental in LN treatment. The authors also found that long-term renal outcomes are mainly associated with renal flares during IS tapering.