Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Efficacy and safety of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: A case series in China
Lancet 2025 Doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(25)01671-X Epub ahead of print
Gao et al. report that allogeneic CAR NK-cell therapy is a potent option for treatment of autoimmune diseases and may address limitations of current autologous CAR T-cell therapy, including manufacturing scale and time, access, safety, and cost. Authors evaluated the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of allogeneic CD19 CAR NK-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory SLE.
Keywords:
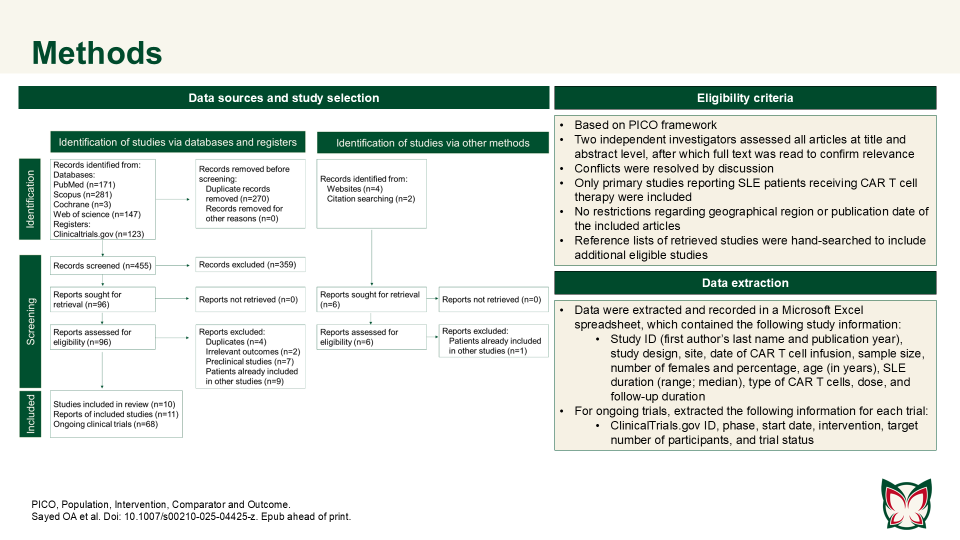
CAR T cell therapy efficacy and safety in SLE: A systematic review and pooled analysis of 47 patients across 10 studies
Doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04425-z
Sayed OA et al. reported that CAR T cell therapy showed promise in refractory SLE, achieving durable remission with manageable toxicity; however further trials are needed to confirm long-term outcomes. Authors consolidated the current evidence on CAR T cell therapy in the treatment of SLE.
BCMA-targeted CAR T cell therapy can effectively induce disease remission in refractory lupus nephritis
Ann Rheum Dis 2025;0:1−9
Hu et al. report that anti-BCMA only CAR T cell can help LN patients safely and effectively, indicating its potential to be a feasible therapeutic strategy in treating autoimmune diseases with abnormal humoral immune responses.
Unsupervised machine learning identifies distinct systemic lupus erythematosus patient endotypes with differential response to belimumab
Rheumatol (Oxford), 2025 DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf215. Epub ahead of print
Depascale et al. used unsupervised machine learning to identify three SLE endotypes based on B cell immunophenotyping and serological profiles. Belimumab was most effective in patients with transitional and naïve B cell enrichment (Cluster 2), where it significantly increased the likelihood of achieving sustained LLDAS and DORIS remission.
Keywords:
LLDAS and remission attainment with anifrolumab treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the TULIP and long-term extension randomised controlled trials
Ann Rheum Dis. 2025:S0003-496700071-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.01.016. Epub ahead of print
Morand et al. conducted a post-hoc analysis of the phase III TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials and their long-term extension, including 369 patients with moderate to severe SLE, to evaluate the long-term impact of anifrolumab on attainment of LLDAS and DORIS-defined remission. The results demonstrated that anifrolumab significantly improved the likelihood, speed, and duration of LLDAS and DORIS remission versus placebo over 4 years, with benefits sustained throughout the treatment period.
Keywords:
Belimumab versus telitacicept in sequential treatment after rituximab for refractory lupus nephritis: A real-world multicentre study
Lupus Science & Medicine, 2025;12:e001296 DOI:10.1136/lupus-2024-001296
Chen et al. demonstrated that sequential treatment with belimumab or telitacicept following rituximab (RTX) is a potential therapeutic approach for treating refractory LN. Major AEs included immunoglobin deficiency, respiratory tract infections and urinary tract infections, which are consistent with previous studies.
Association of lupus low disease activity state and remission with reduced organ damage and flare in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with high disease activity
Rheumatology 2024; Epub ahead of print DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae631
Kandane-Rathnayake et al. demonstrated that achieving Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) or remission in patients with high disease activity status (HDAS) significantly reduces the risk of organ damage accrual and flares. However, HDAS was found to be a poor prognostic indicator as fewer patients with HDAS attained and sustained LLDAS or remission when compared with non-HDAS patients.
Keywords:
Urinary soluble CD163 is useful as "liquid biopsy" marker in lupus nephritis at both diagnosis and follow-up to predict impending flares
J Transl Autoimmun 2024;9:100244 DOI 10.1016/j.jtauto.2024.100244
Renaudineau, et al. show that the urinary sCD163/creatinurea ratio is a parameter than can be used in addition to anti-dsDNA antibodies, anti-C1q antibodies, C3 complement fraction, the protein excretion to creatinine ratio and the estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Keywords:
Association of sustained lupus low disease activity state with improved outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus: a multinational prospective cohort study
Lancet Rheumatol 2024:S2665-9913(24)00121-8 DOI 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00121-8 Epub ahead of print
This study by Golder, et al. showed a significant protective association of lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) and remission against damage accrual and flare. The authors also found a threshold of 3 months sustained LLDAS or remission, and that 3 months of sustained LLDAS are attainable in the setting of a 6–12-month clinical trial.
Keywords:
CD19 CAR T-Cell therapy in autoimmune disease - A case series with follow-up
N Engl J Med 2024;390(8):687–700 DOI 10.1056/NEJMoa2308917
In this case series by Müller, et al., eight patients who received a CD19 CAR T-cell infusion achieved Definition of Remission in SLE (DORIS) remission, Lupus Low Disease Activity State and a SLEDAI 2K score of 0 at 6 months post-infusion. Long-term follow-up through 24 months showed that SLE disease activity remained absent
in all eight patients.