Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
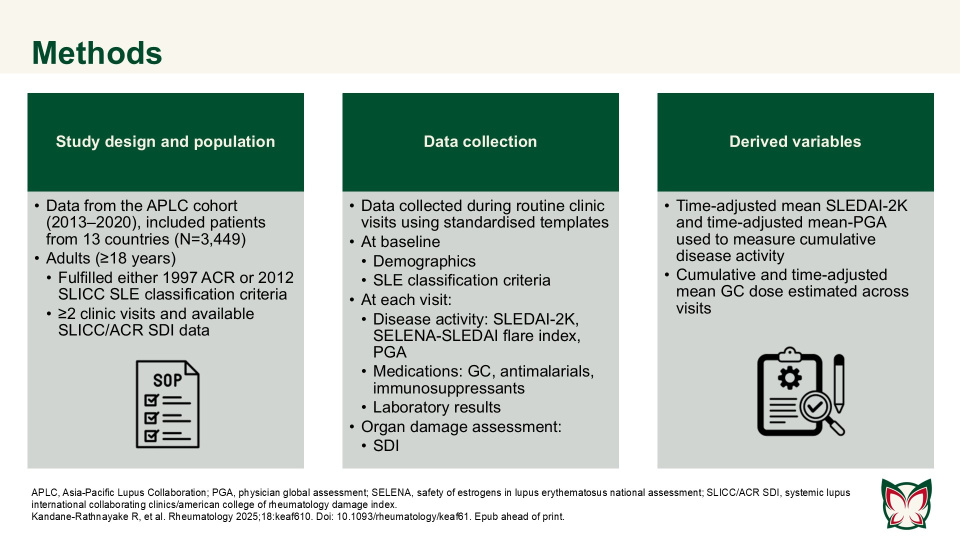
Predictors of damage accrual by organ domain in systemic lupus erythematosus
Rheumatology 2025;18:keaf610 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf610 Epub ahead of print
Kandane-Rathnayake et al. reported that risk factors for individual organ system damage were highly varied in patients with SLE, and not all factors associated with domain-specific damage were captured by summed systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/american college of rheumatology damage index (SLICC/ACR SDI) for overall organ damage.
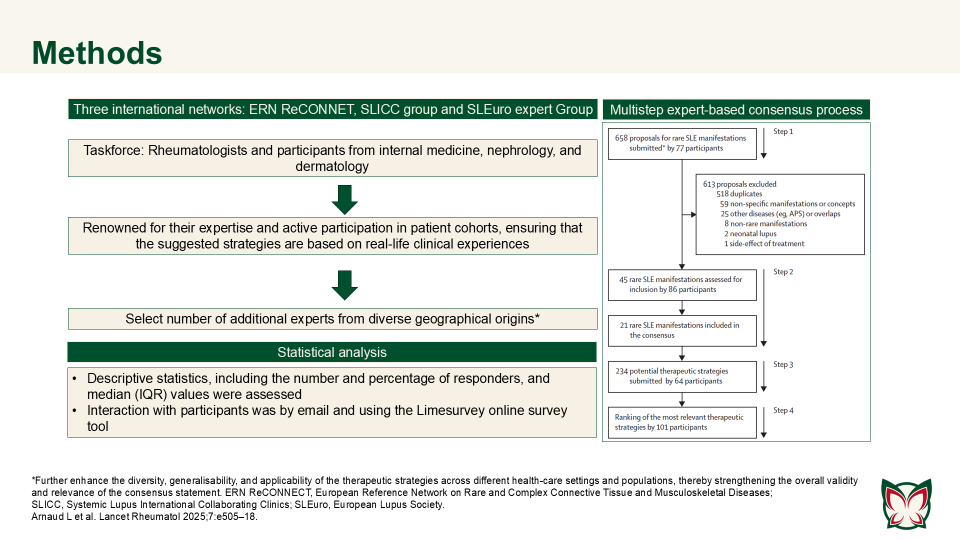
ERN ReCONNET–SLICC–SLEuro expert consensus on the therapeutic management of rare systemic lupus erythematosus manifestations
Lancet Rheumatol 2025;7:e505–18 Doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(25)00063-3
This systematic review highlighted the major gaps in evidence regarding rare SLE manifestations, with many findings dependent on variable methodologies or single reports. Arnard et al. established an international consensus on therapeutic strategies for rare SLE manifestations.
Keywords:
LLDAS and remission attainment with anifrolumab treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the TULIP and long-term extension randomised controlled trials
Ann Rheum Dis. 2025:S0003-496700071-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.01.016. Epub ahead of print
Morand et al. conducted a post-hoc analysis of the phase III TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials and their long-term extension, including 369 patients with moderate to severe SLE, to evaluate the long-term impact of anifrolumab on attainment of LLDAS and DORIS-defined remission. The results demonstrated that anifrolumab significantly improved the likelihood, speed, and duration of LLDAS and DORIS remission versus placebo over 4 years, with benefits sustained throughout the treatment period.
Keywords:
Association of lupus low disease activity state and remission with reduced organ damage and flare in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with high disease activity
Rheumatology 2024; Epub ahead of print DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae631
Kandane-Rathnayake et al. demonstrated that achieving Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) or remission in patients with high disease activity status (HDAS) significantly reduces the risk of organ damage accrual and flares. However, HDAS was found to be a poor prognostic indicator as fewer patients with HDAS attained and sustained LLDAS or remission when compared with non-HDAS patients.
Keywords:
Association of sustained lupus low disease activity state with improved outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus: a multinational prospective cohort study
Lancet Rheumatol 2024:S2665-9913(24)00121-8 DOI 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00121-8 Epub ahead of print
This study by Golder, et al. showed a significant protective association of lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) and remission against damage accrual and flare. The authors also found a threshold of 3 months sustained LLDAS or remission, and that 3 months of sustained LLDAS are attainable in the setting of a 6–12-month clinical trial.
Keywords:
Smith-specific regulatory T cells halt the progression of lupus nephritis
Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 6;15(1):899 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45056-x
Compared with polyclonal mock-transduced regulatory T cells (Tregs), Smith(Sm)-Tregs potently suppress Sm-specific pro-inflammatory responses in vitro and suppress disease progression in a humanised mouse model of lupus nephritis.
Keywords:
Type I interferon blockade with anifrolumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus modulates key immunopathological pathways in a gene expression and proteomic analysis of two Phase 3 trials
Ann Rheum Dis 2024 DOI 10.1136/ard-2023-225445 Epub ahead of print https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38569851/
Type I IFN blockade with anifrolumab modulated multiple inflammatory pathways downstream of type I IFN signalling.
Risk of flare and damage accrual after tapering glucocorticoids in modified serologically active clinically quiescent patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A multinational observational cohort study
Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Feb 29:ard-2023-225369 doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-225369 Epub ahead of print
Flare risk did not increase following glucocorticoid tapering in modified serologically active clinically quiescent patients with SLE. They also found that antimalarial use was associated with decreased flare risk.
Burden of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Clinical Practice: Baseline Data from the SLE Prospective Observational Cohort Study (SPOCS) by Interferon Gene Signature
Lupus Sci Med. 2023; 10(2):e001032 DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2023-001032
This study from Arnaud et al described baseline characteristics of SLE patients grouped by disease activity and IFNGS category in the international SPOCS study. IFNGS-high patients were younger at SLE diagnosis, and a baseline SLEDAI-2K score ≥10 was associated with shorter disease duration, more frequent and more severe flares. IFNGS-low patients were more likely to exhibit musculoskeletal and CNS comorbidities than IFNGS-high patients. Continuation of the SPOCS study will allow investigation into how different baseline characteristics affect long-term outcomes in SLE patients.
Keywords:
EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: 2023 Update
Ann Rheum Dis 2023;83(1):15–29 DOI: 10.1136/ard-2023-224762
The objective of this international task force was to update the EULAR recommendations for the management of SLE. The Task Force agreed on 5 overarching principles and 13 recommendations, generating an overall framework for the approach to a patient with SLE. The updated recommendations provide consensus guidance on the management of SLE, combining evidence and expert opinion.