Publications
Find coverage of the latest original articles on Lupus, focusing on those with data on therapeutic interventions and those that have clinical impact.
Predictors of damage accrual by organ domain in systemic lupus erythematosus
Rheumatology 2025;18:keaf610 Doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf610 Epub ahead of print
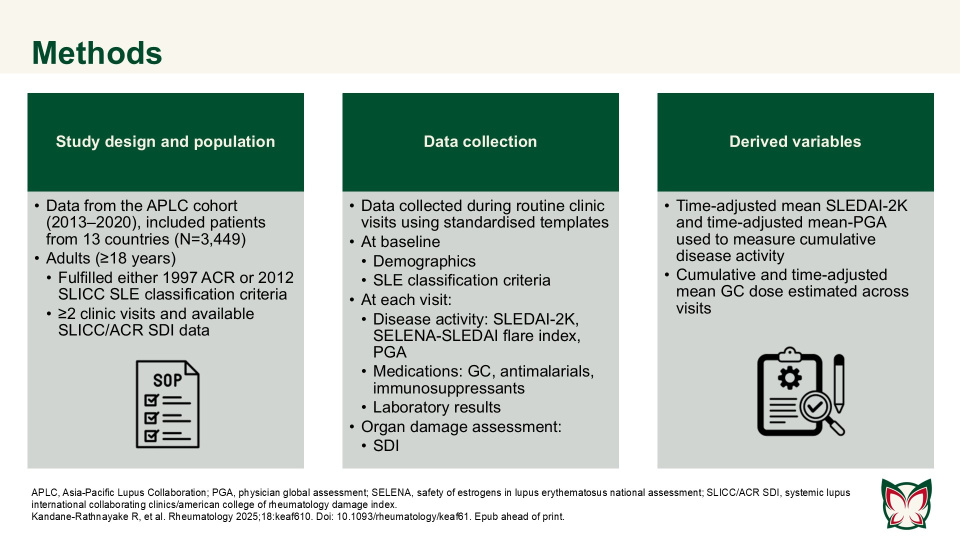
Kandane-Rathnayake et al. reported that risk factors for individual organ system damage were highly varied in patients with SLE, and not all factors associated with domain-specific damage were captured by summed systemic lupus international collaborating clinics/american college of rheumatology damage index (SLICC/ACR SDI) for overall organ damage.
Association of lupus low disease activity state and remission with reduced organ damage and flare in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with high disease activity
Rheumatology 2024; Epub ahead of print DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae631
Kandane-Rathnayake et al. demonstrated that achieving Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) or remission in patients with high disease activity status (HDAS) significantly reduces the risk of organ damage accrual and flares. However, HDAS was found to be a poor prognostic indicator as fewer patients with HDAS attained and sustained LLDAS or remission when compared with non-HDAS patients.
Keywords:
Association of sustained lupus low disease activity state with improved outcomes in systemic lupus erythematosus: a multinational prospective cohort study
Lancet Rheumatol 2024:S2665-9913(24)00121-8 DOI 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00121-8 Epub ahead of print
This study by Golder, et al. showed a significant protective association of lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) and remission against damage accrual and flare. The authors also found a threshold of 3 months sustained LLDAS or remission, and that 3 months of sustained LLDAS are attainable in the setting of a 6–12-month clinical trial.
Keywords:
Belimumab Corticosteroid‑Sparing Treatment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Real‑Life Observational Study (BESST)
Rheumatol. Int. 2024 Apr 30:1–7 DOI: 10.1007/s00296-024-05589-2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38687385/
Belimumab confers an early and sustained corticosteroid-sparing effect after 3 months of treatment in SLE patients. This was demonstrated by a significant prednisone dose reduction that continued through months 6 and 12, and was sustained until month 24.
Lupus low disease activity state and organ damage in relation to quality of life in systemic lupus erythematosus: A cohort study with up to 11 years of follow-up
Rheumatology 2024 DOI 10.1093/rheumatology/keae120 Epub ahead of print
Patients with a lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) irrespective of organ damage were significantly more likely to have favourable health-related quality of life, pain, fatigue, and overall health experience.
Keywords:
Risk of flare and damage accrual after tapering glucocorticoids in modified serologically active clinically quiescent patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A multinational observational cohort study
Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Feb 29:ard-2023-225369 doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-225369 Epub ahead of print
Flare risk did not increase following glucocorticoid tapering in modified serologically active clinically quiescent patients with SLE. They also found that antimalarial use was associated with decreased flare risk.
Association Between Severe Nonadherence to Hydroxychloroquine and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Flares, Damage, and Mortality in 660 Patients From the SLICC Inception Cohort
Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75(12):2195–2206 DOI: 10.1002/art.42645
n this study, severe nonadherence to hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) was independently associated with the risk of SLE flare in the following year, early damage and 5-year mortality.
Keywords:
SGLT2 Inhibitors Alleviated Podocyte Damage in Lupus Nephritis by Decreasing Inflammation and Enhancing Autophagy
Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 DOI: 10.1136/ard-2023-224242
Data revealed a renoprotective effect of SGLT2 inhibitors by reducing proteinuria and preserving renal function in the murine MRL/lpr lupus model.
Relationship Between the EULAR/ACR Classification Criteria and Organ Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus. 2023. doi: 10.1177/09612033231153791
Ambispective cohort study concludes that, in addition to disease classification, the EULAR/ACR SLE criteria may have value in predicting prognosis.
Keywords:
Lupus Low Disease Activity State and Remission and Risk of Mortality in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Prospective, Multinational, Longitudinal Cohort Study
Lancet Rheumatol. 2022. Epub ahead of print. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00304-6
Lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) significantly reduced the risk of mortality in patients with SLE.